Common Pet Parasites: Roundworms, Hookworms, Tapeworms
Roundworms, scientifically known as ascarids, frequently plague both dogs and cats by colonizing their intestinal tracts. These unwelcome guests can trigger concerning symptoms like unusual tiredness, digestive upset, and a distended abdomen. The latter often signals a severe infestation requiring immediate attention.
These parasites lay resilient eggs that contaminate outdoor areas, particularly where pets relieve themselves. This underscores why maintaining hygienic play spaces and regular deworming protocols are non-negotiable for responsible pet care.
Common Internal Parasites: Hookworms
Hookworms present another serious threat, literally latching onto intestinal walls and causing blood loss that may lead to anemia. Affected animals often show decreased energy levels, digestive issues, and noticeable weight reduction. The intensity of these symptoms typically reflects the scale of infestation.
Like other parasites, hookworm larvae thrive in contaminated soil, making environmental vigilance equally important as medical prevention. Consistent preventive care, including scheduled deworming, forms the cornerstone of protection against these blood-sucking pests.
Common Internal Parasites: Tapeworms
Tapeworms stand out with their distinctive segmented bodies, often entering pets through intermediate hosts like fleas or small rodents. Telltale signs include digestive disturbances and visible worm segments in feces. Routine stool examinations help catch these infections early.
Effective treatment requires a dual approach: eliminating the tapeworms themselves while simultaneously addressing any flea problems. Tackling both aspects simultaneously prevents the frustrating cycle of reinfection that plagues many pet owners.
Why Prevention Matters Most
Scheduled deworming, especially during vulnerable growth periods like puppyhood or kittenhood, serves as the first line of defense. This proactive stance not only safeguards pet health but also proves far more economical than treating full-blown infestations later.
Identifying and Addressing Parasites
Veterinary professionals rely on thorough examinations and microscopic stool analysis to pinpoint parasitic infections. These diagnostics guide tailored treatment plans that consider both the specific parasite involved and the patient's overall health status.
Creating a Hostile Environment for Parasites
Regular sanitation of pet areas—from outdoor spaces to bedding—drastically reduces parasite risks. Proper waste management and consistent flea control work synergistically to break the transmission cycle, offering long-term protection for your entire household.
Tapeworms: Recognizing the Segments
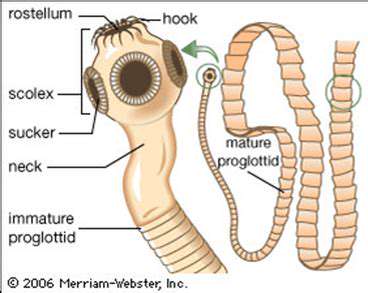
Spotting the Telltale Segments
Tapeworms possess a unique segmented anatomy that makes them instantly recognizable to trained eyes. These repeating units, called proglottids, serve as miniature reproductive factories, each containing complete sets of reproductive organs. This segmentation represents an evolutionary masterpiece that ensures the parasite's survival across generations.
Proglottid morphology varies dramatically between tapeworm species, with some displaying simple structures while others boast intricate designs. These variations provide valuable clues for species identification and help researchers unravel the complex life cycles of these persistent parasites.
The Science Behind Segmentation
This segmented design isn't merely aesthetic—it's a brilliant reproductive strategy. By producing countless independent reproductive units, tapeworms achieve exponential breeding potential, explaining their success across diverse ecosystems and host species.
Each segment undergoes gradual maturation, systematically developing reproductive capabilities before detaching to spread eggs. This staggered development ensures continuous propagation, a key factor in the parasite's persistent presence in animal populations.
The controlled release of egg-laden segments represents the culmination of the tapeworm's life cycle, enabling it to jump to new hosts and continue its species. Understanding this process remains critical for developing targeted interventions against these tenacious parasites.