Managing Pet Allergies Through Diet
Food allergies present significant health challenges for many individuals globally. Recognizing the triggers and implementing effective identification techniques is vital for both prevention and management. A careful, systematic approach is necessary, involving detailed symptom analysis, potential allergen awareness, and proper testing procedures.
Frequent Food Allergens: Detailed Examination
Certain foods commonly cause allergic reactions, including peanuts, tree nuts (such as almonds and walnuts), dairy, eggs, soy, wheat, fish, and shellfish. Recognizing these prevalent allergens helps minimize reaction risks.
Note that this list isn't comprehensive, as other foods may also provoke allergic responses.
Recognizing Allergic Reactions: Signs and Trends
Identifying allergic reaction symptoms is crucial for timely response. Reactions may appear as hives, swelling, breathing difficulties, or digestive problems. Tracking symptom patterns helps isolate potential allergens.
The time between food consumption and symptom onset provides valuable diagnostic clues.
The Value of Comprehensive Food Records
Maintaining detailed food records is fundamental for allergen identification. This includes documenting all consumed foods, specific ingredients, preparation techniques, and timing. Such thorough records reveal patterns that might otherwise go unnoticed.
Using Elimination Diets for Allergy Identification
Elimination diets serve as effective tools for pinpointing allergens. These involve temporarily removing suspected foods and observing symptom changes. Careful planning and monitoring during this process yield clear insights about problematic foods. Consistent symptom tracking proves essential.
The Importance of Medical Allergy Testing
While elimination diets offer helpful information, professional tests like skin prick or blood tests provide definitive allergy confirmation. These objective assessments enable precise diagnoses and customized treatment plans, particularly for severe or complex cases.
Strategies for Allergy Management and Prevention
After identifying allergens, implement management strategies including strict avoidance, careful label reading, and cross-contamination awareness. Education about risks and proper protocols ensures effective allergy control.
The Role of Hypoallergenic Diets in Managing Pet Allergies
Understanding Human Reactions to Pets
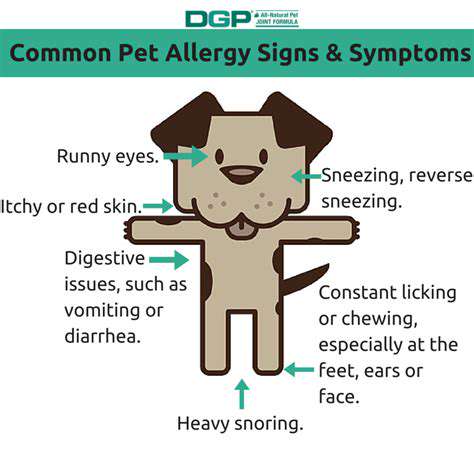
Pet allergies affect numerous individuals worldwide, resulting from immune system overreactions to proteins in pet dander, saliva, urine, and fur. These microscopic proteins become airborne, triggering allergic responses in sensitive people. Identifying specific triggers enables better management approaches.
Reactions range from mild discomfort to severe respiratory distress, including sneezing, runny nose, itchy eyes, skin rashes, and breathing difficulties. Determining the exact pet causing allergies helps create effective management plans.
Pinpointing Allergens: More Than Just Pets
While pets often cause reactions, environmental factors like dust mites, pollen, and mold spores can also trigger or worsen symptoms. Accurate identification of all contributing factors proves essential.
Sometimes allergens aren't obvious, as individual sensitivities and exposure levels create complex reaction patterns. Thorough evaluation ensures personalized management strategies.
The Science of Hypoallergenic Pet Nutrition
Hypoallergenic pet diets don't treat human allergies directly but may reduce problematic proteins in pet dander, saliva, and urine. While not a cure, this approach can decrease allergic reaction potential.
Implementing Hypoallergenic Diets
These specialized pet foods often use novel or highly processed protein sources to minimize common allergens. The goal is reducing exposure to proteins triggering human reactions.
However, effectiveness varies by individual sensitivity. A hypoallergenic diet might not eliminate all symptoms since people react to different proteins.
Veterinary Consultation Importance
Always consult a veterinarian before starting hypoallergenic diets. They assess pets' nutritional needs and recommend safe, balanced options while explaining potential benefits and limitations.
Veterinarians can also identify other contributing factors, creating comprehensive strategies addressing both pet and human needs.
Comprehensive Allergy Management Approaches
Hypoallergenic diets form just one part of allergy management. Additional measures like air purifiers, thorough cleaning, and environmental adjustments significantly reduce allergen exposure. Combined strategies typically yield best results.
Integrating dietary changes with environmental controls improves overall pet allergy management.
Dietary Changes and Their Impact on Pet Allergy Symptoms
Nutritional Considerations in Dietary Changes
Diet modifications, whether for health, weight, or lifestyle reasons, substantially affect nutrient intake. These changes can create deficiencies or excesses of vitamins, minerals, and macronutrients, impacting overall health. Understanding food choices' nutritional implications maintains optimal health. Diverse, balanced diets ensure proper nutrient intake.
Dietary changes require careful evaluation of food sources and their nutrient profiles. For instance, vegetarian or vegan diets may need vitamin B12 supplements, while processed food-heavy diets can lead to unhealthy fat, sugar, and sodium excess.
Weight Management Through Diet
Dietary adjustments frequently support weight management goals. Balanced nutrition with exercise helps achieve healthy weight. Focusing on whole foods rather than processed alternatives, which often contain excess calories and unhealthy fats, proves most effective. Weight changes directly relate to dietary modifications.
Adjusting calorie intake, portion sizes, and food types supports weight goals. Reduced calories with increased activity typically leads to weight loss, while increased calories may cause weight gain. Sustainable management combines dietary and lifestyle changes.
Diet's Role in Chronic Disease Prevention
Diet significantly influences chronic disease risks like heart disease, diabetes, and certain cancers. Diets rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains lower these risks. Conversely, diets high in saturated/trans fats, refined sugars, and processed foods increase disease likelihood. Informed food choices prevent conditions.
Diet modifications help manage existing conditions. Diabetics may adjust carbohydrate intake, while heart disease patients might limit unhealthy fats.
Digestive Health and Dietary Changes
Diet substantially affects gastrointestinal function. High-fiber diets from fruits, vegetables, and whole grains promote digestion and prevent constipation. Low-fiber diets may cause bloating, gas, and discomfort. Certain foods worsen conditions like irritable bowel syndrome.
Adding or removing specific foods impacts digestion. Lactose intolerance responds to dairy avoidance, while gluten intolerance requires eliminating gluten-containing foods. Recognizing individual sensitivities maintains digestive health.
Psychological Aspects of Dietary Changes
Diet modifications affect mental well-being. Sudden or extreme changes may cause deprivation feelings, cravings, or distress. Psychological impact depends on coping abilities and support systems. Addressing emotional aspects ensures long-term dietary success.
Social and Cultural Dietary Factors
Social and cultural norms influence dietary habits, determining food choices and preparation methods. Dietary changes may require adapting to new social contexts, which can prove challenging. Support helps navigate these adjustments.
Dietary choices might affect relationships if not handled sensitively. Strict diets may require social gathering modifications. Open communication eases these social transitions.
Long-Term Health Effects of Dietary Changes
Sustained dietary changes produce varied long-term health outcomes. Consistent healthy eating improves overall health, reduces chronic disease risks, and enhances well-being. Conversely, prolonged unhealthy eating harms physical and mental health. Commitment ensures lasting benefits.
Long-term dietary changes affect cardiovascular health, cognitive function, and more. Regular monitoring and adjustments optimize outcomes.
Culturally competent mental health services development addresses health disparities effectively. This requires deep understanding of diverse cultural backgrounds, beliefs, and experiences in mental health care. Genuine commitment to respecting individual needs surpasses surface-level awareness. Culturally competent providers engage in continuous learning and self-reflection to deliver equitable care, recognizing cultural factors' impact on mental health presentation and treatment adherence.