Understanding Lighting in Pet Photography: Essential Tips
Understanding Shadows and Highlighting in Pet Photography
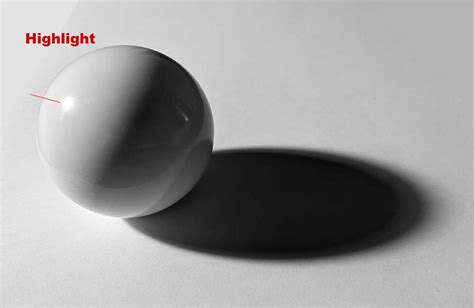
Understanding the Role of Shadows
Shadows play a crucial role in shaping our perception of three-dimensional objects. They define form and volume, adding depth and realism to images and scenes. By observing how light falls on an object and creates shadows, we can better understand its shape and position relative to the light source. The interplay of light and shadow is a fundamental aspect of visual communication, helping us to interpret the world around us.
Shadows not only reveal shape but also provide critical information about the environment. Their direction and length can tell us about the position of the light source, whether it's the sun, a lamp, or another light source. Understanding these subtle cues can help us determine the time of day, the type of lighting, and even the location of the light source in a scene.
Highlighing the Importance of Highlighting
Highlighs, the areas of an object that receive the most direct light, are just as important to a scene as the shadows themselves. They provide a crucial visual anchor, pulling the viewer's eye to key elements and drawing attention to specific features. The intensity and quality of highlighting can significantly impact the overall mood and atmosphere of a work, whether it's a painting, a photograph, or a 3D model.
Highlighs dramatically enhance the visual appeal of an object by creating a sense of luminosity and texture. The way light reflects off a surface, creating highlights, allows us to perceive the surface's material properties, such as smoothness, shininess, or roughness. The placement of highlights is essential for creating a sense of realism and sophistication.
Analyzing the Relationship Between Shadows and Highlights
The interplay between shadows and highlights is essential for creating a sense of depth and volume in any visual representation. Understanding how these elements work together allows artists and designers to create compelling images that effectively communicate form and texture. By carefully considering the placement and intensity of both shadows and highlights, artists can convey a sense of realism and enhance the visual impact of their work.
A strong understanding of the relationship between shadows and highlights is critical for creating a realistic and compelling image. The subtle gradations and transitions between light and shadow contribute to the overall visual richness and depth of a scene. A skillful manipulation of these elements can create a sense of drama and emotion, drawing the viewer into the artwork.
Post-Processing for Enhanced Pet Portraits

Pre-processing for Image Enhancement
Image pre-processing is a crucial step in any image enhancement pipeline. It involves a series of operations to prepare the input image for subsequent processing steps. This includes tasks such as noise reduction, contrast adjustment, and color correction. Proper pre-processing can significantly improve the quality and reliability of subsequent analysis and feature extraction. For example, reducing noise in images of pets can dramatically improve the accuracy of object detection algorithms.
Careful consideration must be given to the choice of pre-processing techniques. Different techniques are suitable for different types of images and noise characteristics. The selection of pre-processing steps should be tailored to the specific application and the characteristics of the input images, such as pet images. Optimizing these initial steps can often have a cascading effect, leading to improvements throughout the entire processing chain.
Sharpening and Detail Enhancement
Sharpening techniques are often employed to enhance details and edges in images, which is particularly important for pet images where precise features like fur texture and eye shape are critical. These techniques aim to increase the contrast between different regions of the image, making subtle details more apparent.
High-pass filters are frequently utilized for sharpening. These filters effectively highlight the high-frequency components of the image, which correspond to the edges and fine details. By amplifying these components, the overall image clarity and sharpness are improved, leading to a more visually appealing and informative representation of the pet.
Color Correction and Enhancement
Color correction is essential for ensuring that the colors in the image are accurate and consistent. Inadequate color correction can lead to inaccurate representation of the pet's coat color or other details. For example, a pet with a multicolored coat may appear washed out or have incorrect color balance if the image is not properly color-corrected.
Color enhancement techniques can further improve the visual appeal of the image, making it more vibrant and lifelike. These techniques often involve adjusting the color saturation, hue, and brightness. Careful application of these techniques can help to emphasize the characteristics of the pet, such as a rich and vibrant fur color or distinctive eye color.
Noise Reduction and Artifact Removal
Noise reduction techniques are vital for removing unwanted artifacts from images, such as those caused by sensor imperfections or image acquisition issues. These techniques can effectively reduce the graininess or other distortions in pet images. Reducing noise is crucial for accurate feature extraction and analysis, especially in low-light or low-resolution images. Noise can make it difficult to discern subtle details and patterns in the image.
Advanced filtering techniques can be used to remove noise while preserving the important features of the pet. These techniques often rely on statistical models or machine learning algorithms to identify and remove noisy regions while preserving sharp edges and textures. This careful noise reduction process is essential for maintaining the integrity of the image data and ensuring accurate analysis.
Read more about Understanding Lighting in Pet Photography: Essential Tips
Hot Recommendations
- Customized Sleep Schedules: AI Driven for Sustainable Rest
- Crafting a Personalized Productivity Plan for Mental Clarity
- Sustainable Self Compassion: Cultivating Kindness Towards Your Mind
- Sustainable Productivity Hacks for the Busy Professional
- Sustainable Wellness for Parents: Balancing Family and Self Care
- Data Informed Self Care: Designing Your Personalized Wellness Strategy
- Sustainable Wellness for a Purpose Driven Life
- AI Assisted Mindfulness: Personalized Meditations for Deeper Practice
- Building Inclusive Mental Health Services: Key Initiatives
- AI Powered Self Care: Customizing Your Routine for Maximum Impact