Hydrolyzed Protein Diets: When Are They Necessary?
What are Hydrolyzed Proteins?

Understanding Hydrolyzed Proteins
Hydrolyzed proteins are proteins that undergo a breakdown process into smaller peptides and individual amino acids. This transformation, known as hydrolysis, occurs through either chemical reactions or enzymatic activity. The resulting smaller fragments allow for significantly improved absorption within the human body when compared to intact protein molecules.
The enhanced bioavailability of these protein fragments makes them particularly valuable for people experiencing digestive challenges or those requiring rapid nutrient uptake. These modified proteins deliver a potent concentration of essential amino acids, which play vital roles in tissue repair, muscular development, and numerous physiological processes.
Varieties of Hydrolyzed Protein Formulations
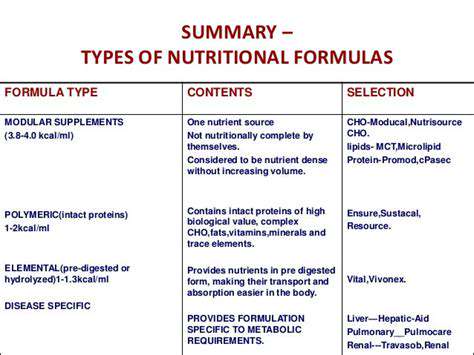
Numerous protein sources can undergo the hydrolysis process, yielding different protein hydrolysates. Common examples include modified versions of whey, casein, and plant-based proteins like soy. Each variant possesses distinct properties that determine its suitability for various nutritional applications.
Whey protein hydrolysate stands out for its exceptionally fast absorption characteristics, making it a preferred choice among athletic populations needing immediate post-exercise recovery. Casein hydrolysate provides a contrasting benefit with its prolonged amino acid release pattern, supporting extended periods between meals.
Nutritional Advantages of Protein Hydrolysates
The reduced molecular size of hydrolyzed proteins enables accelerated digestive processing and nutrient assimilation. This efficient metabolic pathway facilitates prompt delivery of amino acids to muscle tissues, potentially enhancing recovery periods following physical exertion and supporting optimal muscle remodeling.
The documented benefits for tissue regeneration and muscular development represent key reasons for the popularity of these specialized protein forms. Ongoing clinical investigations continue to examine their broader implications for human health and nutritional therapy.
Digestive Efficiency and Metabolic Utilization
Protein hydrolysates demonstrate superior digestive tolerance compared to whole protein structures. Their partially pre-digested nature allows for more rapid uptake and utilization of amino acids by bodily systems.
This improved digestive profile proves especially advantageous for individuals with compromised digestion or those experiencing difficulties processing complete protein molecules. The smaller peptide chains readily pass through intestinal membranes with minimal digestive effort required.
Practical Applications in Nutrition
Hydrolyzed proteins have become fundamental components in various nutritional supplements and fortified food products. Manufacturers frequently incorporate them into specialized formulations like recovery beverages, protein-enriched snacks, and meal replacement options designed to support active lifestyles.
The optimized amino acid composition renders these proteins particularly appealing to fitness enthusiasts, competitive athletes, and health-conscious consumers pursuing precise nutritional strategies. Beyond sports nutrition, medical applications are being explored for specialized dietary interventions and therapeutic nutrition programs.
Safety Profile and Usage Considerations
While generally recognized as safe for most populations, some individuals might experience transient digestive symptoms including abdominal distension or gastrointestinal discomfort. Individual responses and potential sensitivities should guide personal usage patterns.
Consultation with qualified healthcare providers or nutrition specialists is recommended before making significant dietary modifications involving hydrolyzed protein products, particularly for individuals managing chronic health conditions.
Comparative Analysis with Intact Proteins
Evaluating hydrolyzed proteins alongside whole protein sources reveals fundamental differences in biological impact. The modified proteins provide accelerated nutrient delivery and potentially enhanced anabolic responses due to their structural characteristics.
Complete proteins offer more comprehensive nutrient profiles and typically demonstrate extended release kinetics. Optimal selection depends on individual metabolic requirements, timing considerations, and specific health objectives.
Read more about Hydrolyzed Protein Diets: When Are They Necessary?
Hot Recommendations
- Customized Sleep Schedules: AI Driven for Sustainable Rest
- Crafting a Personalized Productivity Plan for Mental Clarity
- Sustainable Self Compassion: Cultivating Kindness Towards Your Mind
- Sustainable Productivity Hacks for the Busy Professional
- Sustainable Wellness for Parents: Balancing Family and Self Care
- Data Informed Self Care: Designing Your Personalized Wellness Strategy
- Sustainable Wellness for a Purpose Driven Life
- AI Assisted Mindfulness: Personalized Meditations for Deeper Practice
- Building Inclusive Mental Health Services: Key Initiatives
- AI Powered Self Care: Customizing Your Routine for Maximum Impact