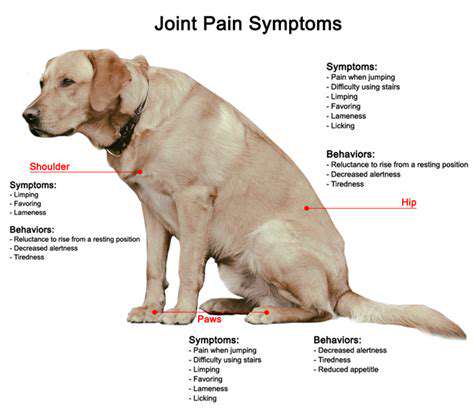
Stem Cell Therapy for Arthritis in Dogs
Stem cell therapy presents a promising avenue for managing canine arthritis. Stem cells are undifferentiated cells with the remarkable ability to differentiate into various specialized cell types, including cartilage cells. Clinical trials and studies on stem cell therapy in dogs are exploring its potential to promote cartilage repair, reduce inflammation, and alleviate pain associated with arthritis. However, further research is needed to fully understand the long-term efficacy and safety of this approach.
While promising, stem cell therapy is not a guaranteed cure for canine arthritis. It's important to discuss the potential benefits and risks of this treatment with your veterinarian to determine if it's an appropriate option for your dog. Individual responses to stem cell therapy can vary, and a thorough understanding of the treatment process is crucial before considering it.
Types of Stem Cells Used in Canine Arthritis Treatment
Embryonic Stem Cells
Embryonic stem cells (ESCs) are derived from the inner cell mass of a developing embryo. These cells possess the remarkable ability to differentiate into virtually any cell type within the body. This pluripotency makes them highly attractive for therapeutic applications in canine medicine. However, ethical concerns surrounding the use of embryos are significant and must be carefully considered in the context of canine treatment.
The process of isolating and culturing ESCs is complex and requires specialized laboratory techniques. Furthermore, the long-term safety and efficacy of ESC-based therapies in dogs remain a subject of ongoing research and development. Careful monitoring and evaluation are crucial throughout the entire process.
Adult Stem Cells
Adult stem cells, also known as somatic stem cells, are found in various tissues throughout the adult canine body. These cells are responsible for maintaining and repairing tissues and organs, and they have the potential to differentiate into specific cell types within their respective tissue lineages. Unlike embryonic stem cells, they are readily available and pose fewer ethical concerns.
A key advantage of adult stem cells is their relative ease of isolation and their demonstrated ability to contribute to tissue regeneration and repair. However, their differentiation potential is typically limited compared to ESCs, meaning they may not be suitable for all therapeutic applications. Further research is needed to fully understand their potential and limitations.
Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs)
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are a type of adult stem cell found in various canine tissues, including bone marrow, adipose tissue, and umbilical cord blood. These cells are particularly promising for regenerative medicine due to their ability to differentiate into various cell types, including cartilage, bone, and fat. This versatility makes them a valuable tool for treating various canine musculoskeletal disorders.
MSCs have shown promising results in preclinical studies for treating canine osteoarthritis and other joint conditions. Clinical trials are ongoing to further evaluate their safety and efficacy in canine patients. The ability to potentially address the root cause of debilitating conditions is a major draw.
Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells (iPSCs)
Induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) are adult cells that have been reprogrammed to an embryonic-like pluripotent state. This process involves introducing specific genes into adult cells, which can be done using various methods. This method potentially overcomes ethical issues associated with the use of embryonic stem cells. However, the safety and long-term efficacy of iPSCs in canine therapies still require further investigation.
The reprogramming process itself can be complex and costly, and the long-term stability of iPSCs needs to be carefully assessed. Furthermore, the exact mechanisms of iPSC differentiation are not entirely understood, which limits their potential in certain applications.
Umbilical Cord Blood Stem Cells
Umbilical cord blood (UCB) is a rich source of stem cells, including hematopoietic stem cells, which are crucial for blood cell production. These cells are readily available from canine umbilical cords after birth. The collection process is relatively straightforward and poses minimal risk to the mother and the offspring. UCB stem cells have shown promise in treating various canine hematological disorders.
The use of UCB stem cells in canine therapy is a relatively new area of research, but early findings suggest potential benefits in treating conditions such as immune deficiencies and certain types of leukemia. These cells are easily accessible and offer a potentially valuable source of treatment.
Neural Stem Cells
Neural stem cells (NSCs) are a specialized type of stem cell that have the potential to differentiate into various types of neurons and glial cells within the canine central nervous system. They play a crucial role in maintaining and repairing the damaged nervous tissue. The study of NSCs is important for understanding and potentially treating canine neurological disorders.
NSCs hold significant promise for treating conditions like canine spinal cord injuries and neurodegenerative diseases. More research is needed to fully understand their potential and limitations in treating these complex conditions.
Considerations and Limitations of Stem Cell Therapy
Ethical Considerations
Stem cell therapy, while holding immense promise, raises significant ethical concerns. The sourcing of stem cells, particularly embryonic stem cells, often involves the destruction of embryos, sparking debate about the moral status of a developing organism. Furthermore, the potential for misuse, such as the creation of designer babies or the commodification of human life, necessitates careful ethical oversight and stringent regulations to prevent exploitation. These considerations are crucial for ensuring the responsible and equitable application of this powerful technology, and they must be addressed alongside the clinical benefits.
The potential for unintended consequences in stem cell therapies also necessitates careful ethical analysis. For example, the possibility of immune rejection reactions, tumor formation, or the long-term effects of introducing foreign cells into the body must be thoroughly investigated and addressed. This requires extensive research and rigorous clinical trials to minimize risks and maximize patient safety. Equally important is the equitable access to this potentially life-altering treatment, ensuring that it's not limited to the wealthy or privileged while addressing potential disparities in access based on socioeconomic factors.
Clinical Limitations and Challenges
Despite the promising preclinical data, stem cell therapy for arthritis faces significant clinical limitations. The precise mechanisms by which stem cells exert their therapeutic effects remain incompletely understood. Therefore, accurately predicting treatment outcomes and tailoring therapies to individual patients presents a considerable challenge. Furthermore, the complex regulatory landscape governing stem cell therapies varies considerably between jurisdictions, creating obstacles in the widespread adoption and implementation of this potentially transformative treatment.
The practical challenges of stem cell therapy are also substantial. The isolation, expansion, and delivery of appropriate stem cells for clinical use remain technically demanding. This often involves sophisticated laboratory procedures and specialized personnel, which can increase costs and limit accessibility. Moreover, the long-term efficacy and safety of stem cell therapy need to be further validated through rigorous and extended clinical trials to ensure that the benefits outweigh the risks in the long term. These limitations highlight the need for continued research and development to overcome these practical hurdles.
Cost-effectiveness is another crucial limitation. The specialized equipment, skilled personnel, and multiple procedures involved in stem cell therapy can significantly increase the overall cost of treatment. This economic barrier could limit access for many patients, potentially exacerbating existing health disparities. Addressing these cost concerns is essential to ensure that stem cell therapy becomes a viable and accessible option for a broader range of patients. Developing more cost-effective methodologies is crucial to making it more widely available.
Safety and Risk Assessment
Safety concerns are paramount in stem cell therapy. The introduction of foreign cells into the body carries the risk of immune rejection, tumor formation, or other adverse reactions. Rigorous preclinical testing and rigorous clinical trials are essential to minimize these risks and ensure patient safety. Monitoring long-term effects is equally critical to identify any potential late-onset complications and adapt treatment strategies accordingly. This necessitates a comprehensive understanding of the biological processes involved and the potential for unpredictable interactions with the patient's immune system.
Specific risks associated with different stem cell types and delivery methods need careful evaluation. For instance, the potential for the stem cells to migrate to unintended locations, or for the cells to differentiate into undesirable cell types, must be addressed with specific strategies. Careful consideration of the patient's individual medical history and any existing conditions is also critical to mitigate potential risks. Each patient's unique circumstances must be considered to tailor the treatment plan to minimize adverse events.