The Ethics of AI in Pet Care: What to Consider
The Future of Responsible AI in Pet Care
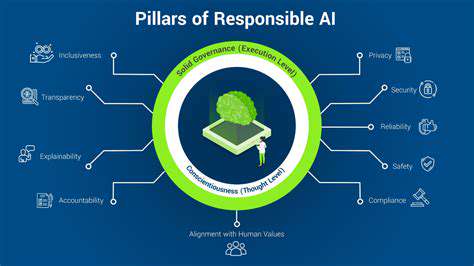
Ethical Considerations in AI Development
As AI systems become increasingly sophisticated, the ethical implications of their development and deployment become paramount. Developers must prioritize fairness, transparency, and accountability in their design processes. This involves careful consideration of potential biases in training data, ensuring that AI systems don't perpetuate or exacerbate existing societal inequalities, and building in mechanisms for human oversight and intervention where necessary.
These ethical considerations extend beyond the technical aspects of AI development. The societal impact of AI must also be thoroughly evaluated, considering its potential impact on employment, privacy, and the very fabric of human interaction. Open dialogue and collaboration between researchers, policymakers, and the public are crucial to navigating these complexities.
Bias Mitigation and Fairness
One of the most pressing concerns surrounding AI is the potential for bias in algorithms. Biased training data can lead to discriminatory outcomes, perpetuating existing inequalities in areas like loan applications, criminal justice, and even hiring processes. Therefore, rigorous methodologies for identifying and mitigating bias must be developed and implemented in AI development pipelines.
Techniques for data pre-processing, algorithm design, and evaluation metrics can help identify and counteract these biases. This requires an ongoing commitment to data diversity and a willingness to confront uncomfortable truths about existing societal inequalities.
Transparency and Explainability
Understanding how AI systems arrive at their decisions is crucial for building trust and ensuring accountability. Black box algorithms, where the decision-making process is opaque, can be problematic, hindering human understanding and oversight. Developing explainable AI (XAI) techniques is essential for fostering trust and ensuring responsible use.
This includes providing clear and concise explanations for the decisions made by AI systems, making them more accessible and understandable for both technical experts and the general public. Such transparency is vital for ensuring that AI systems are used ethically and in accordance with human values.
Data Privacy and Security
The collection and use of personal data in AI systems raise significant privacy concerns. Robust data security measures and privacy policies are critical to protect sensitive information from unauthorized access or misuse. Protecting individual privacy while leveraging the potential of AI presents a significant challenge requiring innovative solutions.
Human-AI Collaboration
The future of AI likely involves a symbiotic relationship between humans and AI. AI can augment human capabilities, allowing us to perform tasks more efficiently and effectively. This collaboration requires careful consideration of how to design AI systems that complement, rather than replace, human roles and responsibilities.
Focus must be placed on ensuring AI systems are designed to support human decision-making and offer assistance, rather than making independent decisions without human oversight.
Regulatory Frameworks and Governance
Establishing clear regulatory frameworks and governance structures is essential to ensure responsible AI development and deployment. Governments and international organizations must work together to develop guidelines that promote ethical AI practices and address potential risks. This includes setting standards for data privacy, bias mitigation, and transparency in AI systems.
These frameworks should be adaptable to the evolving nature of AI technology, allowing for continuous improvement and refinement as AI systems become more complex.
Accessibility and Inclusivity
AI systems should be designed to be accessible and inclusive, ensuring that they can be used by people from all backgrounds and with diverse needs. This includes considering factors like language barriers, disabilities, and cultural differences. Failing to address accessibility and inclusivity can create significant disadvantages and perpetuate existing inequalities.
AI systems should be designed to be usable by everyone, fostering a more equitable and inclusive future.
Read more about The Ethics of AI in Pet Care: What to Consider
Hot Recommendations
- Customized Sleep Schedules: AI Driven for Sustainable Rest
- Crafting a Personalized Productivity Plan for Mental Clarity
- Sustainable Self Compassion: Cultivating Kindness Towards Your Mind
- Sustainable Productivity Hacks for the Busy Professional
- Sustainable Wellness for Parents: Balancing Family and Self Care
- Data Informed Self Care: Designing Your Personalized Wellness Strategy
- Sustainable Wellness for a Purpose Driven Life
- AI Assisted Mindfulness: Personalized Meditations for Deeper Practice
- Building Inclusive Mental Health Services: Key Initiatives
- AI Powered Self Care: Customizing Your Routine for Maximum Impact