Vaccinations for Pets: Protecting Your Companion
Choosing the Right Vaccination Schedule for Your Pet
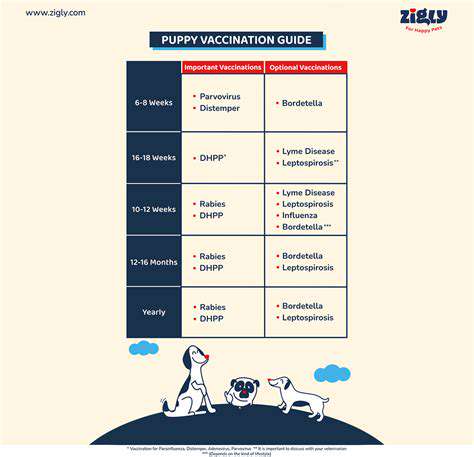
Understanding Vaccination Schedules
Vaccination schedules are meticulously designed to provide optimal protection against various infectious diseases throughout a person's life. These schedules are not arbitrary; they are developed by public health experts and scientists based on years of research and data analysis. Understanding the rationale behind these schedules is crucial for making informed decisions about vaccination. This ensures that the body's immune response is maximized at the most effective stages of development. The timing of vaccinations is carefully considered to capitalize on the developing immune system's capacity to effectively fight off pathogens.
Different vaccines require different intervals for optimal immune response. Some vaccines are administered in a series over time to build a robust and long-lasting immunity. Others are given as single doses, but even these are carefully timed to ensure maximum effectiveness. The schedules are constantly reviewed and updated as new research emerges, ensuring that the recommendations remain aligned with the latest scientific understanding of disease prevention.
Factors Influencing Vaccination Choices
Several factors can influence a person's vaccination choices. These include personal health history, potential allergies, and pre-existing medical conditions. Individuals with weakened immune systems, such as those undergoing chemotherapy or with certain chronic illnesses, may require different vaccination schedules or alternative considerations. These factors are crucial to evaluate when determining the most appropriate vaccination schedule for an individual.
Lifestyle choices, such as travel plans and exposure to certain populations, may also play a role in vaccination decisions. For example, individuals traveling to regions with high rates of certain infectious diseases may need additional or adjusted vaccinations. Furthermore, certain occupations might necessitate specific vaccinations to prevent occupational exposure to pathogens.
Consulting with a healthcare professional is always recommended to discuss individual needs and potential risks associated with various vaccination schedules. An informed discussion with a doctor or other qualified healthcare provider is essential in making well-informed choices about vaccinations.
Importance of Adherence to Schedules
Adhering to recommended vaccination schedules is vital for individual and community health. Consistent vaccination protects not only the vaccinated individual but also contributes to herd immunity, protecting those who cannot be vaccinated, such as infants and immunocompromised individuals. This collective immunity significantly reduces the risk of outbreaks and protects vulnerable populations. Maintaining a consistent schedule ensures that individuals are shielded from preventable illnesses, which can significantly impact their quality of life and overall well-being.
Missing or delaying vaccinations can compromise the effectiveness of the immune response, increasing the risk of contracting vaccine-preventable diseases. It can also put a strain on healthcare resources and potentially lead to outbreaks, affecting the entire community. This highlights the importance of responsible and proactive engagement with the recommended vaccination schedules.
Considerations for Specific Populations
Vaccination schedules are often tailored to different demographics, including infants, children, adolescents, and adults. The evolving immune system of infants and children necessitates specific vaccination schedules designed to optimize protection against age-appropriate diseases. Adolescents and adults also have unique needs and exposure risks, influencing their vaccination schedules. For example, adolescents might require vaccinations against diseases specific to this life stage, while adults may require boosters to maintain immunity against diseases they were vaccinated against in childhood.
Specific considerations must also be given to pregnant individuals, as well as those with chronic health conditions. Healthcare providers play a vital role in educating and guiding these individuals regarding appropriate vaccination choices and schedules to ensure both their safety and the health of their families or communities.

Read more about Vaccinations for Pets: Protecting Your Companion
Hot Recommendations
- Customized Sleep Schedules: AI Driven for Sustainable Rest
- Crafting a Personalized Productivity Plan for Mental Clarity
- Sustainable Self Compassion: Cultivating Kindness Towards Your Mind
- Sustainable Productivity Hacks for the Busy Professional
- Sustainable Wellness for Parents: Balancing Family and Self Care
- Data Informed Self Care: Designing Your Personalized Wellness Strategy
- Sustainable Wellness for a Purpose Driven Life
- AI Assisted Mindfulness: Personalized Meditations for Deeper Practice
- Building Inclusive Mental Health Services: Key Initiatives
- AI Powered Self Care: Customizing Your Routine for Maximum Impact