Thyroid Disorders in Pets: Diagnosis and Management
Introduction to Thyroid Disorders in Pets
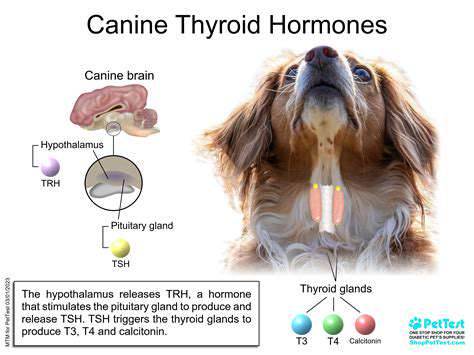
Understanding the Thyroid Gland
Nestled in the lower front of the neck, the thyroid gland resembles a delicate butterfly in shape yet wields tremendous influence over bodily functions. This unassuming organ serves as the body's metabolic thermostat, regulating everything from heart rhythm to energy production. When this gland falters, the consequences ripple through every system, making awareness of its function critical for pet owners. Its subtle yet pervasive effects underscore why veterinarians pay close attention to thyroid health during checkups.
Though small in size, this gland's impact is anything but minor. It operates as a silent conductor, orchestrating a symphony of physiological processes. When its rhythm breaks, the entire body feels the discord, manifesting in ways both obvious and subtle. This explains why thyroid screenings form an essential part of comprehensive veterinary care for aging pets.
Types of Thyroid Disorders
Thyroid dysfunction manifests in two primary forms, each presenting unique challenges for diagnosis and treatment. Hyperthyroidism accelerates bodily processes like an engine stuck in high gear, while hypothyroidism slows everything down like a battery losing charge. What makes these conditions particularly tricky is how differently they can appear from one animal to another, sometimes mimicking other common age-related issues.
Beyond these primary conditions, veterinarians occasionally encounter thyroid nodules or inflammation that require specialized attention. While many cases prove benign, some signal more serious underlying pathology. The key lies in catching these issues early through regular wellness exams before they escalate into major health concerns.
Symptoms of Thyroid Problems
Recognizing thyroid disorders poses challenges because their signs often masquerade as normal aging changes. A previously energetic dog becoming lethargic or a cat shedding weight despite ravenous appetite might both point to thyroid dysfunction. The real art of diagnosis lies in connecting these seemingly unrelated symptoms into a coherent picture, something experienced veterinarians develop through years of practice.
Contrasting presentations highlight the thyroid's complex role. While one pet might pace restlessly with bulging eyes (classic hyperthyroidism), another may sleep excessively with dull fur (characteristic hypothyroidism). This variability explains why pet owners should never dismiss persistent behavioral or physical changes, even if they seem minor at first.
Diagnosis and Treatment Options
Modern veterinary medicine offers multiple pathways for thyroid assessment. Beyond basic blood panels, specialized hormone tests can pinpoint dysfunction with remarkable accuracy. The diagnostic process isn't just about identifying a problem - it's about understanding its root cause and severity, which guides treatment decisions.
Therapeutic approaches vary as widely as the conditions themselves. For overactive thyroids, options range from daily medication to targeted radiation therapy. Underactive glands typically require lifelong hormone supplementation, carefully calibrated through regular blood monitoring. Each treatment path carries distinct advantages that veterinarians weigh against a pet's overall health status.
Living with Thyroid Disorders
Managing thyroid conditions represents an ongoing partnership between pet owners and veterinary teams. Successful outcomes hinge on consistent medication schedules, attentive observation for side effects, and regular progress checks. This commitment to proactive care often makes the difference between adequate control and optimal health, especially for senior pets with multiple medical issues.
The journey doesn't end with diagnosis. Pets thrive when owners become active participants in their care - learning to recognize warning signs, maintaining treatment logs, and communicating openly with their veterinary team. This collaborative approach transforms thyroid management from a medical chore into a rewarding aspect of responsible pet ownership.
Management Strategies for Hyperthyroidism and Hypothyroidism
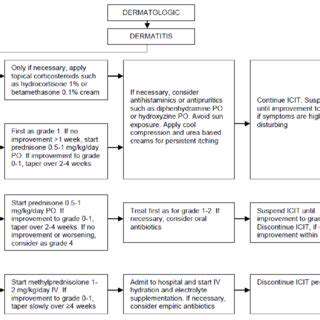
Pharmacological Interventions
When facing hyperthyroidism, medication often serves as the first line of defense. Drugs like methimazole work like microscopic traffic cops, slowing the thyroid's overproduction of hormones. Their effects build gradually, requiring patience and frequent bloodwork to fine-tune dosages. Potential liver impacts mean veterinarians monitor these patients more closely than most.
Radioactive iodine therapy offers a more definitive solution for suitable candidates. This precision treatment targets overactive thyroid cells while sparing healthy tissue, often resolving the condition permanently. The procedure's elegance lies in its specificity - it's like sending microscopic archers to hit only the problematic cells. Post-treatment monitoring ensures no unexpected complications arise during recovery.
Surgical Management
In select cases, surgical removal of the thyroid gland becomes necessary, particularly when medications prove ineffective or tumors develop. This delicate procedure requires a surgeon's steady hands and keen anatomical knowledge. The real challenge lies in preserving the tiny parathyroid glands nearby, which regulate calcium levels independently of thyroid function. When successful, surgery can provide immediate relief from severe symptoms.
Post-operative care introduces new considerations. Most patients require lifelong hormone replacement, transforming one medical management challenge into another. However, for pets struggling with medication side effects or those with cancerous growths, this trade-off often proves worthwhile for restored quality of life.
Lifestyle Modifications
Beyond medical treatments, simple lifestyle adjustments can significantly impact thyroid patients' wellbeing. A diet rich in antioxidants supports overall health while avoiding excessive iodine prevents further gland stimulation. Regular, moderate exercise acts as nature's mood stabilizer, combating both the anxiety of hyperthyroidism and lethargy of hypothyroidism.
Stress reduction techniques benefit thyroid patients disproportionately. The gland responds acutely to stress hormones, creating a vicious cycle of dysfunction. Creating calm environments with predictable routines helps stabilize thyroid function almost as much as some medications, making behavioral interventions a valuable adjunct therapy.
Dietary Considerations
Nutrition plays a nuanced role in thyroid management. While no magic food cures thyroid disease, certain dietary patterns can support treatment efficacy. Monitoring iodine intake proves particularly crucial - too little impairs function, while excess fuels hyperactivity. Many veterinarians now recommend therapeutic diets specifically formulated for thyroid patients.
Individualized nutrition plans account for each pet's unique needs. A hyperthyroid cat might benefit from calorie-dense food to counteract weight loss, while a hypothyroid dog could need portion control to prevent obesity. Working with a veterinary nutritionist ensures dietary changes complement rather than conflict with medical treatments.
Psychological Support
The emotional toll of thyroid disorders often goes unrecognized. Pets may experience confusion from their changing bodies, while owners grapple with caregiving stress. Behavioral therapy can teach coping strategies for pets exhibiting anxiety or aggression secondary to their condition. Simple environmental enrichments often yield dramatic improvements in quality of life.
Support networks provide invaluable resources for overwhelmed owners. Online forums and local support groups create spaces to share practical tips and emotional encouragement. This psychosocial dimension of care completes the holistic approach to thyroid management, addressing the whole patient rather than just their lab results.
Important Considerations for Long-Term Management
Planning and Preparation
Effective thyroid management begins with realistic expectations and clear roadmaps. Charting a course through treatment options requires honest assessments of financial, temporal, and emotional resources. Some paths demand frequent vet visits, while others necessitate strict home monitoring - factors that significantly impact daily life.
Preparation extends beyond medical decisions. Creating organized medication schedules, establishing reminder systems, and designating care responsibilities prevent lapses in treatment. Many successful pet owners develop customized tracking systems that integrate seamlessly into their existing routines.
Resource Allocation and Management
Smart resource allocation separates stressful thyroid management from sustainable care plans. This includes budgeting for recurrent expenses like blood tests and medications while anticipating potential emergencies. Time management proves equally crucial - batching vet visits with other errands or exploring mobile phlebotomy services can dramatically reduce care burdens.
Creative solutions often emerge when resources feel strained. Group purchasing programs, prescription discount cards, and telehealth consultations all offer avenues to stretch limited resources further without compromising care quality.
Risk Assessment and Mitigation
Long-term thyroid management requires anticipating potential complications. Medication side effects, treatment resistance, and concurrent age-related diseases all warrant consideration. Developing contingency plans for these scenarios prevents panic when challenges arise. Many veterinarians help owners create decision trees for common complications.
Proactive measures like maintaining emergency contact lists and preparing go-bags for hospital visits provide peace of mind. Documenting baseline behaviors and normal vitals creates valuable comparison points should problems develop.
Stakeholder Engagement and Communication
Thyroid care succeeds through teamwork. Clear communication channels between veterinarians, veterinary technicians, and family members prevent misunderstandings. Establishing a single point of contact for medical decisions maintains consistency when multiple caregivers are involved. Digital shared calendars and medication logs keep everyone aligned.
Educating all household members about the pet's condition fosters unified care. Even children can learn to recognize warning signs, transforming the entire family into attentive caregivers.
Adaptability and Flexibility
Thyroid management rarely follows a straight path. Treatment plans often require adjustments as pets age or develop new health concerns. The most successful caretakers embrace this fluidity, viewing changes as course corrections rather than failures. Regular checkpoint discussions with veterinarians help identify when modifications might benefit the patient.
Maintaining flexibility extends to care routines themselves. When work schedules change or travel becomes necessary, having backup plans ensures treatment continuity. Many veterinary teams will help design adaptable care plans for these situations.
Monitoring and Evaluation
Consistent tracking transforms subjective observations into actionable data. Simple logs documenting weight trends, energy levels, and medication responses help veterinarians spot patterns invisible during brief clinic visits. Technology like smart scales and activity monitors can automate much of this data collection, creating comprehensive health portraits over time.
Scheduled progress reviews allow owners and veterinarians to assess what's working and what needs refinement. These periodic evaluations often reveal subtle improvements or emerging concerns that daily interactions might miss.
Learning and Improvement
Each stage of thyroid management offers valuable lessons. Documenting successful strategies and challenges creates a personalized knowledge base for future reference. Many pet owners find joining online communities exposes them to innovative solutions they'd never discover independently. Over time, this accumulated wisdom transforms novices into confident care coordinators.
Sharing experiences benefits the wider pet community too. Contributing to support groups or participating in veterinary research helps advance thyroid care for all animals. This collective learning represents perhaps the most rewarding aspect of long-term condition management.
Read more about Thyroid Disorders in Pets: Diagnosis and Management
Hot Recommendations
- Customized Sleep Schedules: AI Driven for Sustainable Rest
- Crafting a Personalized Productivity Plan for Mental Clarity
- Sustainable Self Compassion: Cultivating Kindness Towards Your Mind
- Sustainable Productivity Hacks for the Busy Professional
- Sustainable Wellness for Parents: Balancing Family and Self Care
- Data Informed Self Care: Designing Your Personalized Wellness Strategy
- Sustainable Wellness for a Purpose Driven Life
- AI Assisted Mindfulness: Personalized Meditations for Deeper Practice
- Building Inclusive Mental Health Services: Key Initiatives
- AI Powered Self Care: Customizing Your Routine for Maximum Impact